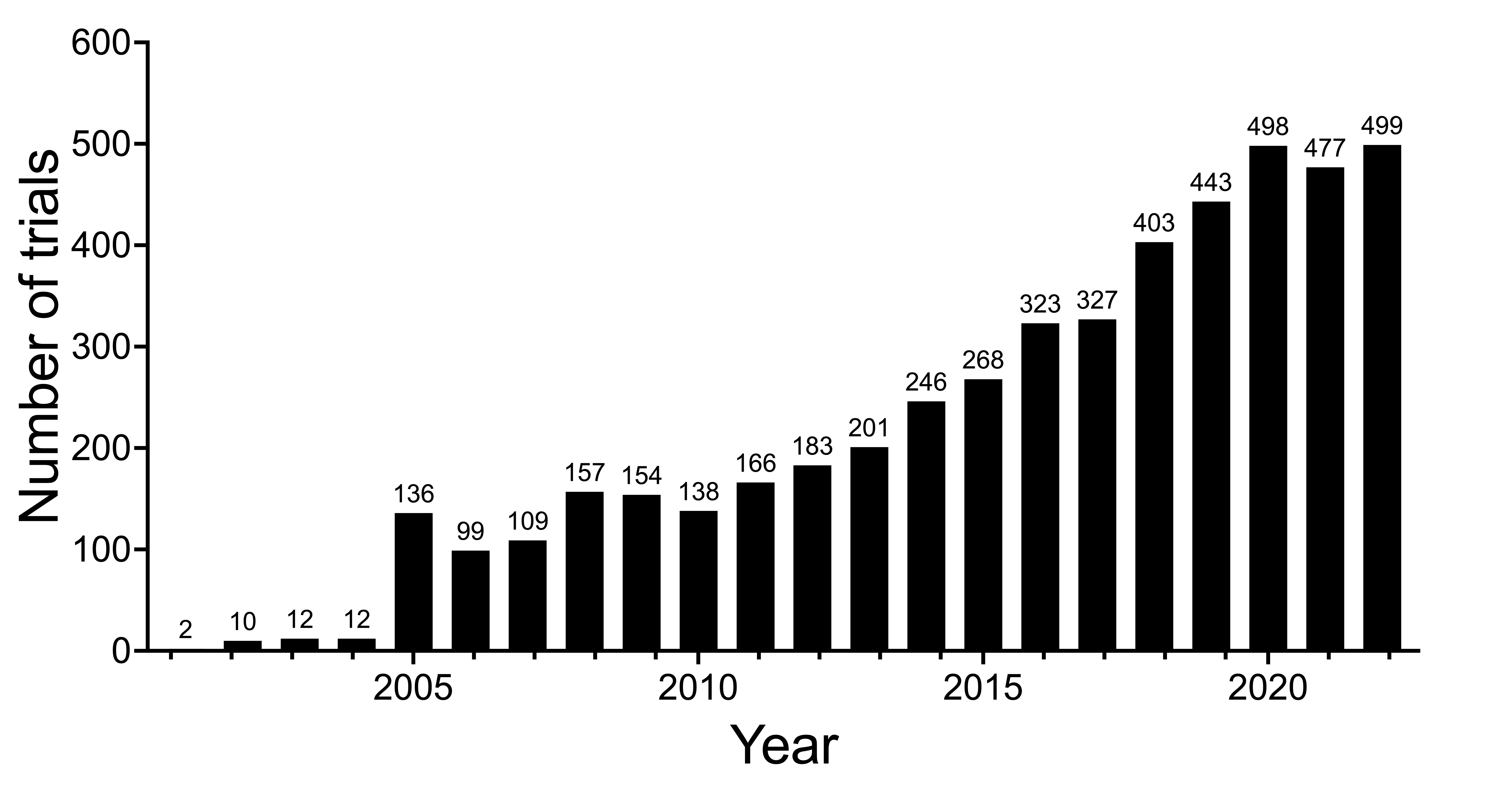
Data collection
Initial search yielded 9,515 trials. Following the data filtering process, instrument annotation, and eligibility assessment, a final data set of 4619 trials were retained for analysis. The submission date of these trials ranged from January 2001 to December 2022.
Figure 1. annural clinical trials
The AD has the highest number of trials with 2163 (46.83%),followed by PD (2013, 43.58%), ALS 177 (396, 8.57%), HD (132, 2.86%), LBD (90, 1.95%) and FTLD (69, 1.49%).
A total of unique 10679 original instrument entities were annotated, which were further mapped to 2494 normalized instruments. The overall average number of instruments employed in trials is 4.4003, while the minimum number is 1 and maximum number is 31. Alzheimer’s disease has the highest number of unique instruments of 1647 with an average of 4.5603 instruments used per trial. FTLD has the highest average number of instruments per trial at 5.3188.
Table 1. Statistic description of clinical trials and outcome measurement instruments
| Neurodegenerative Disease | Number of Trials | Number of Instruments | Number of Unique Instruments | Average Number of Instruments per Trial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD | 2163 | 9864 | 1647 | 4.5603 |
| PD | 2013 | 8245 | 1132 | 4.0959 |
| ALS | 396 | 950 | 223 | 2.3990 |
| HD | 132 | 478 | 166 | 3.6212 |
| LBD | 90 | 421 | 181 | 4.6778 |
| FTLD | 69 | 367 | 185 | 5.3188 |
| Total | 4619 | 20325 | 2494 | 4.4003 |
Shared instruments among NDDs
The AD had the most specific instruments with 1090,194 followed by PD with 649. Among the numerous instruments, 203 were shared between 195 AD trials and PD trials, and 15 were shared across 6 NDDs.
Figure 2. specific and common instruments among 6 neurodegenerative diseases
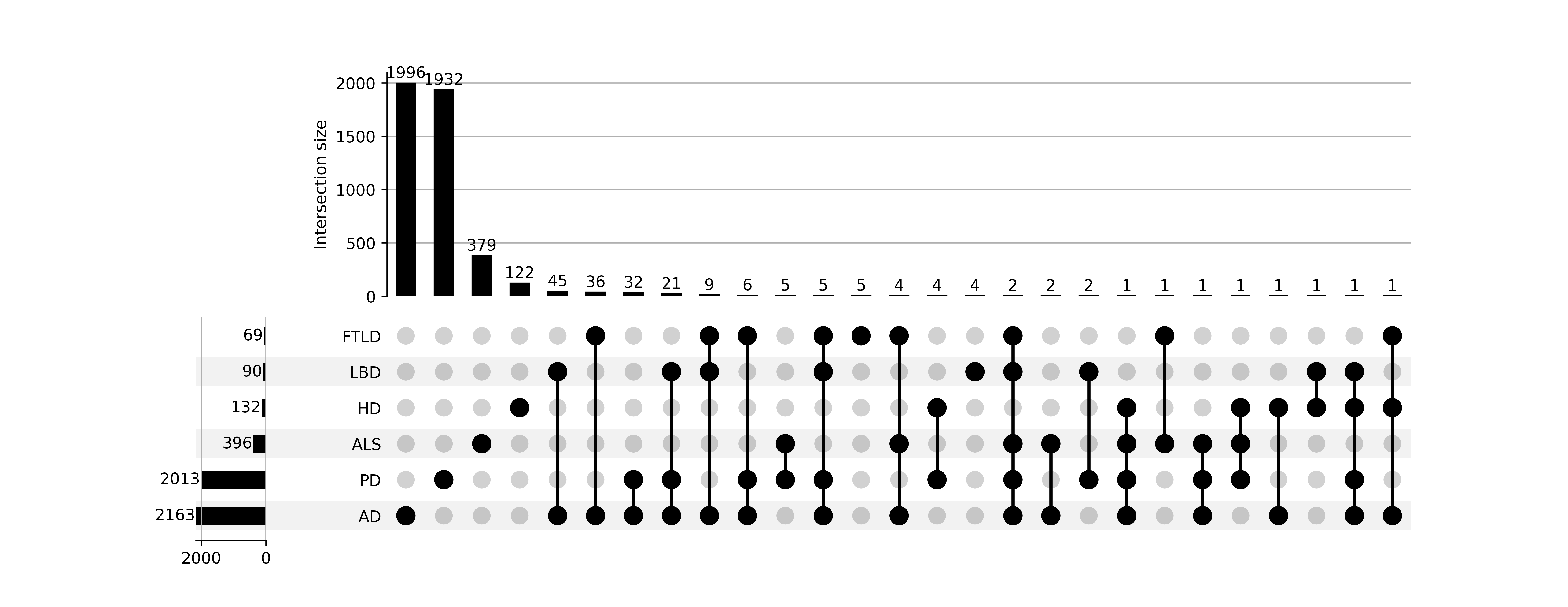
Table 2. 15 outcome measurement instruments employed by 6 common neurodegeneratives diseases.
| Instruments | AD | PD | LBD | HD | ALS | FTLD | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale | 42 | 1315 | 20 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 1390 |
| Mini-Mental State Examination | 725 | 111 | 29 | 6 | 1 | 14 | 886 |
| Neuropsychiatric Inventory | 611 | 42 | 30 | 5 | 5 | 26 | 719 |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment | 196 | 267 | 15 | 14 | 4 | 5 | 501 |
| Clinical Global Impression | 137 | 235 | 9 | 18 | 8 | 12 | 419 |
| Zarit Burden Interview | 240 | 40 | 11 | 2 | 7 | 10 | 310 |
| EQ-5D | 118 | 88 | 4 | 4 | 19 | 2 | 235 |
| Short Form Health Survey | 88 | 64 | 4 | 6 | 11 | 4 | 177 |
| Visual Analogue Scale | 43 | 100 | 2 | 2 | 18 | 2 | 167 |
| Stroop Test | 63 | 57 | 2 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 141 |
| Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale | 55 | 52 | 2 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 131 |
| Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale | 40 | 59 | 5 | 9 | 10 | 2 | 125 |
| Patient Health Questionnaire | 61 | 15 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 95 |
| Verbal Fluency Test | 32 | 17 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 61 |
| Quality of Life in Neurological Disorders | 5 | 17 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 31 |
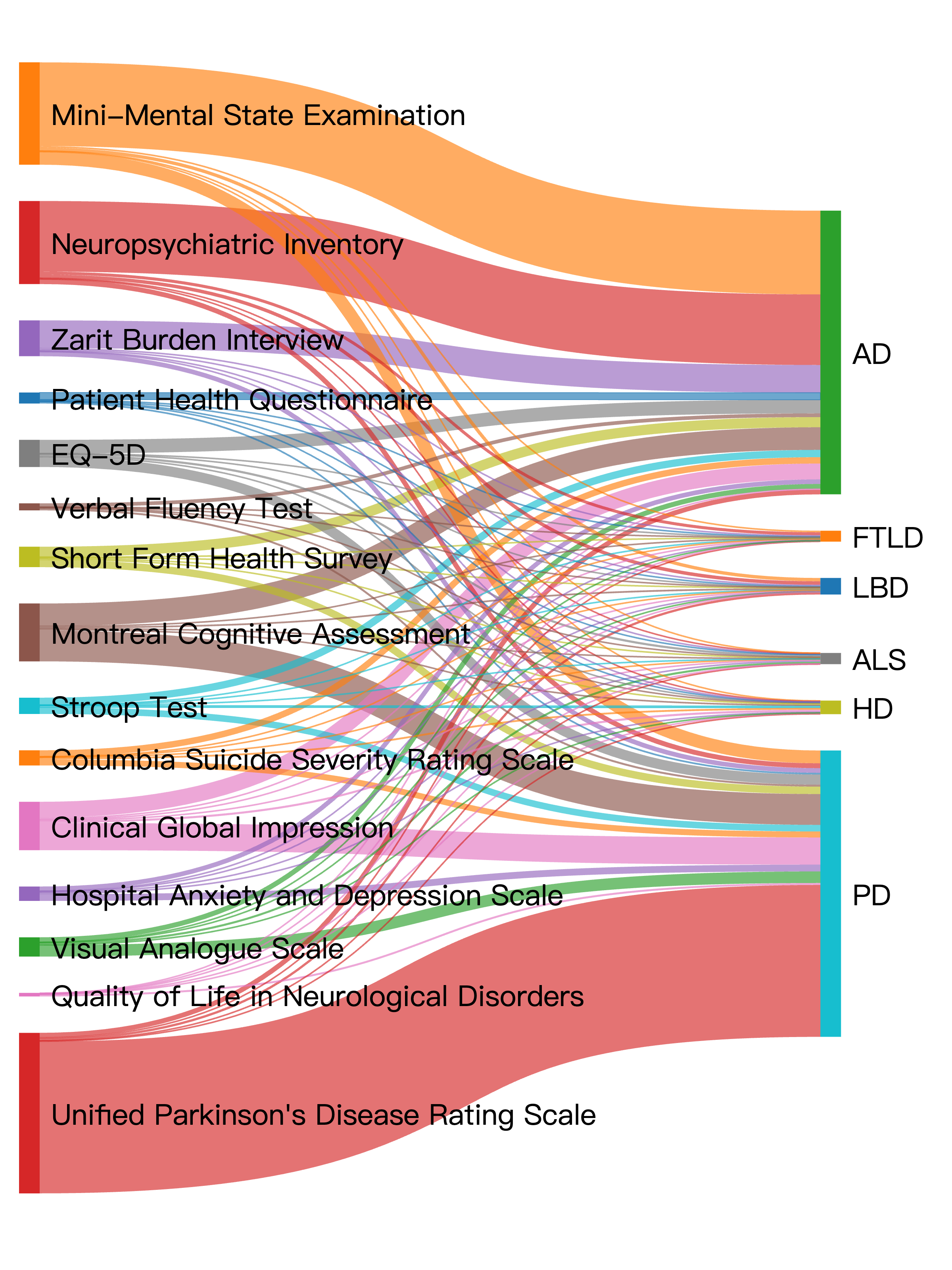
We presented the usage patterns between the 15 instruments and 6 NDDs. The thickness of lines reflects the frequency of usage of each instrument in each disease. We observed a high frequency of usage of the UPDRS for PD. Similarly, MMSE, Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) and Zarit Burden Interview (ZBI) have high frequency usage for AD. Other instruments such as EuroQol 5 Dimensions (EQ-5D), MoCA and Clinical Global Impression (CGI) are often used in both AD and PD, and no significant difference in frequency.
Figure 3. relationships between instruments and neurodegenerative diseases
Temporal trends of the 15 instruments in AD and PD trials, respectively. The results indicated that a majority of the instruments are utilized sparingly, whereas certain instruments are predominant and exhibit increasing usage over time. Specifically, the MMSE in AD trials, while UPDRS in PD trials.
Figure 4. Temporal trends of the 15 instruments in Alzheimer's disease trials
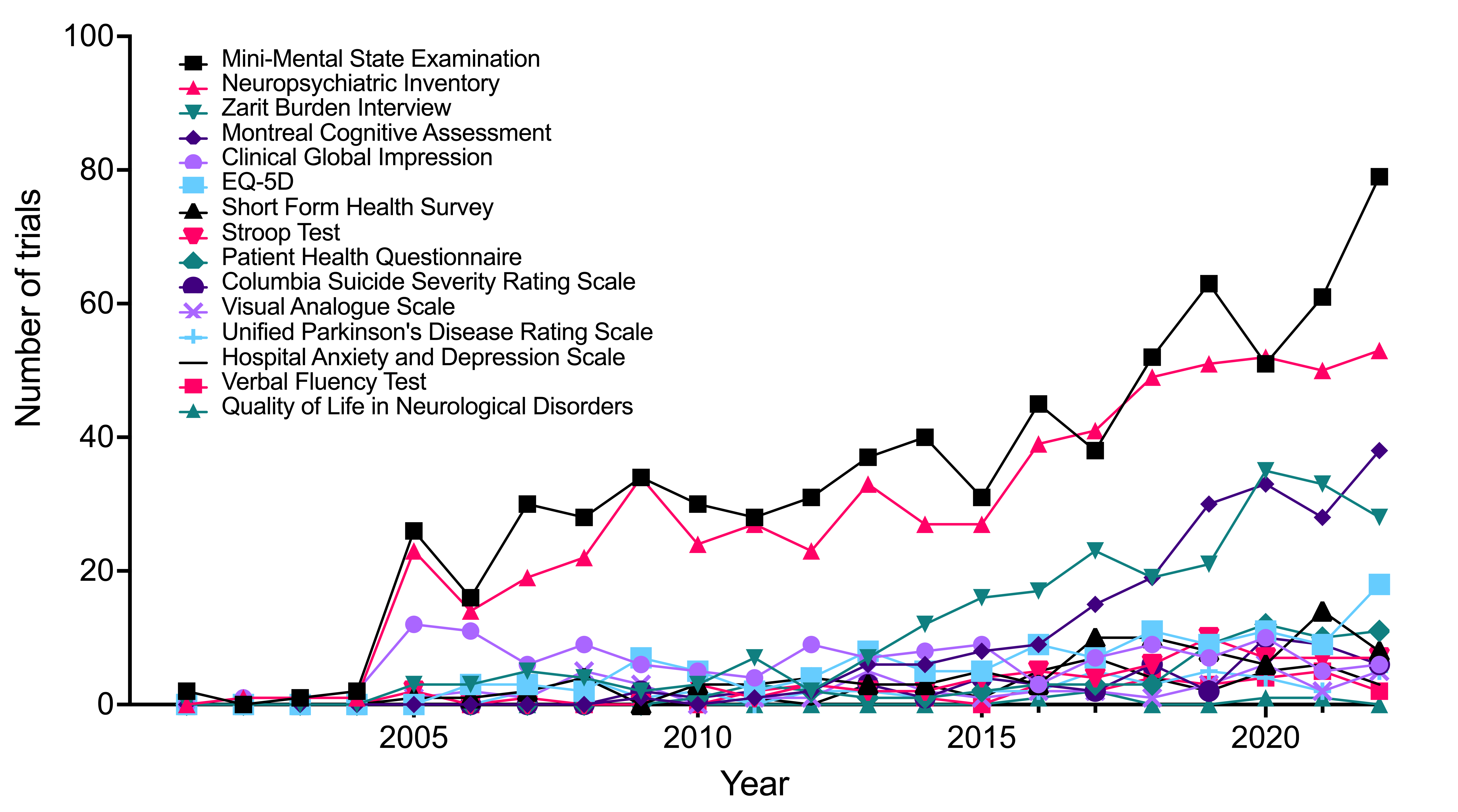
Figure 5. Temporal trends of the 15 instruments in Parkinson's disease trials
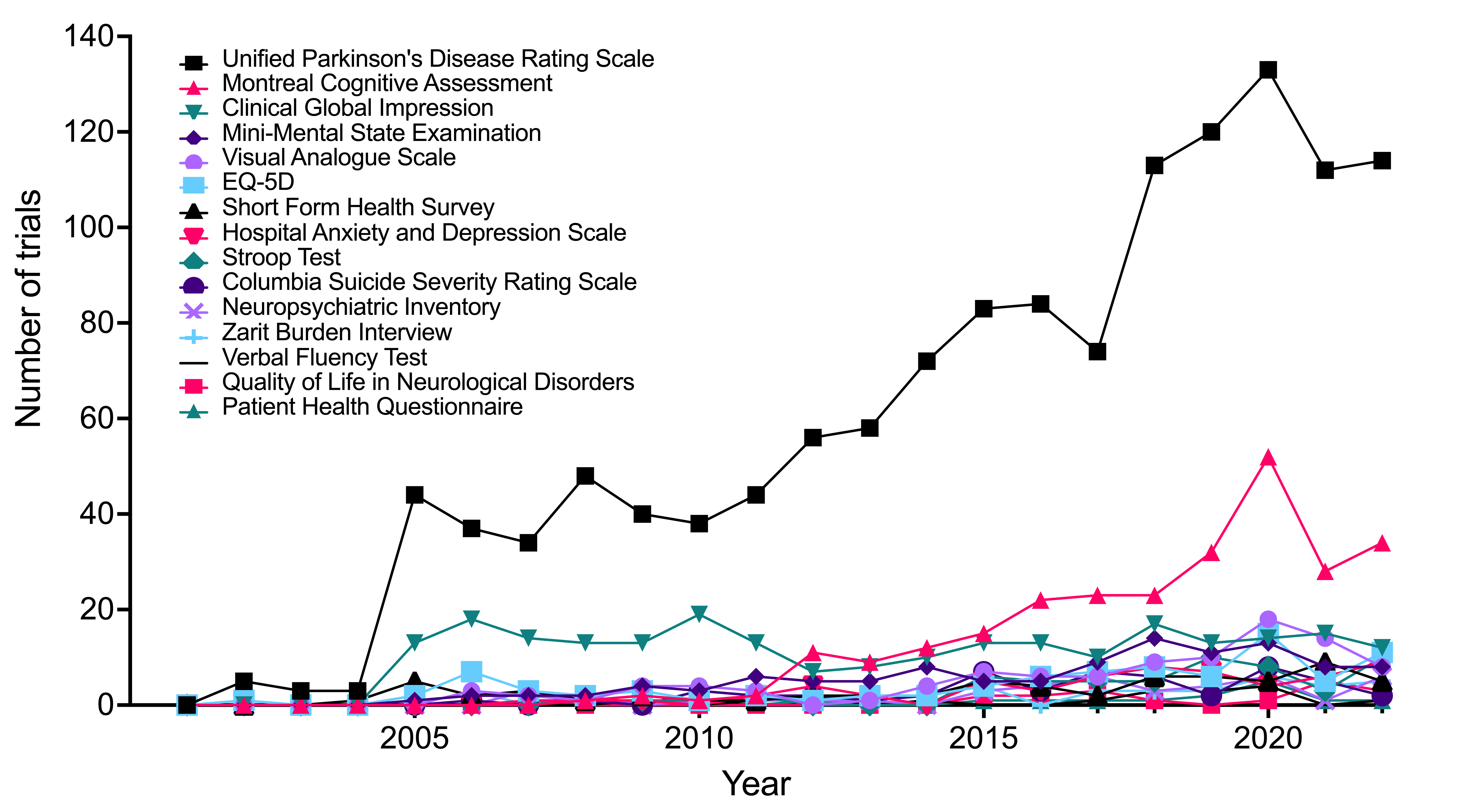
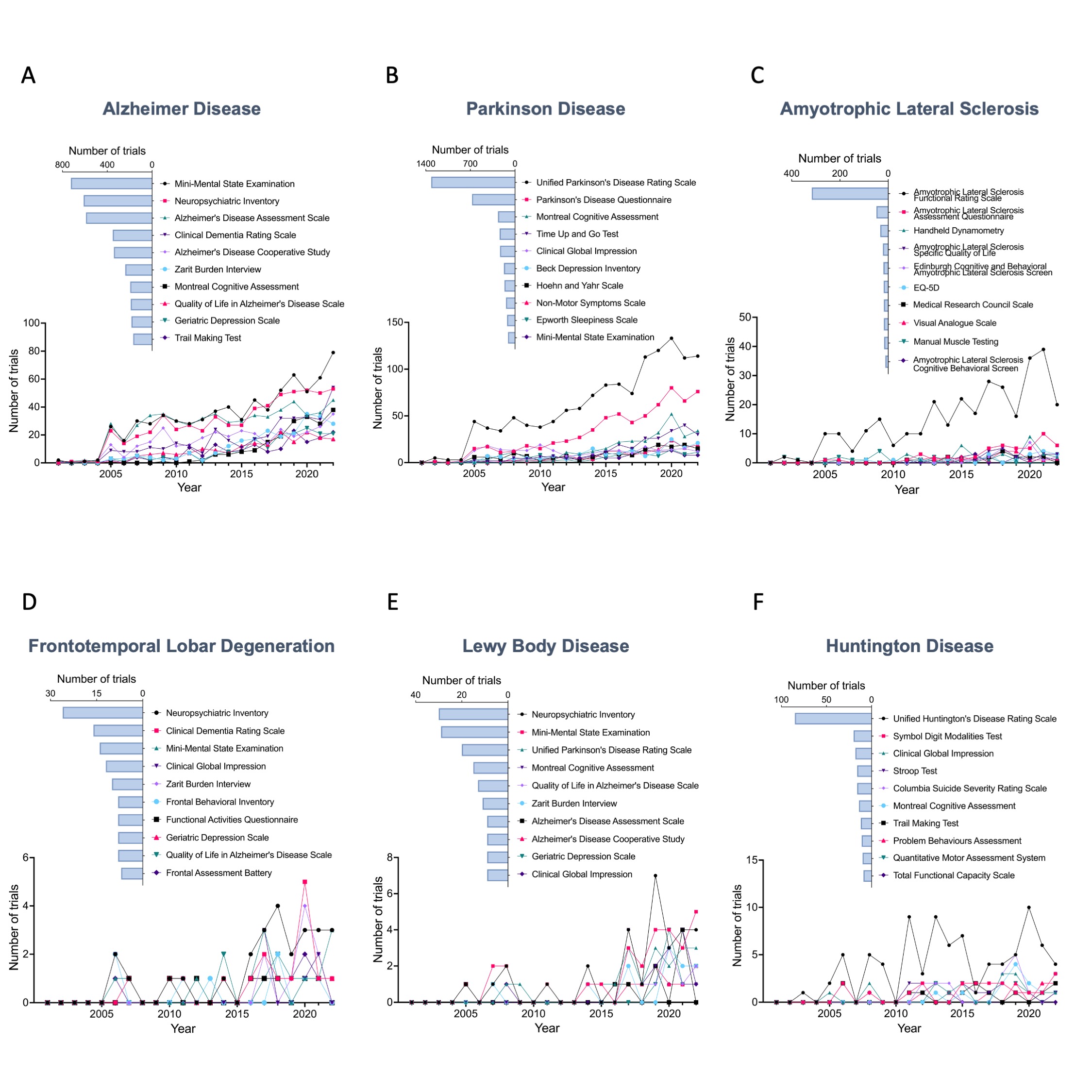
Top popular instruments
The top popular instruments and their usage frequency in temporal trends of each neurodegenerative disease. (A) Alzheimer Disease. (B) Parkinson Disease. (C) Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. (D) Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. (E) Lewy Body Disease. (F) Huntington Disease. In trials targeting AD, the MMSE, NPI, and Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS) are among the most commonly employed instruments. In PD trials, the UPDRS and Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire (PDQ) are most commonly used because they are widely recognized and can offer a thorough evaluation of PD motor and non-motor symptoms. The Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS) occupies an absolute advantage with widespread adoption in ALS research. In contrast, there are relatively fewer studies on FTLD and LBD, and disease-specific instruments are limited.
Figure 6. top popular instruments and their usage frequency in temporal trends of each neurodegenerative disease
Association patterns between different instruments
Over 76.75% of trials employed more than one instruments.In AD trials, ADAS-MMSE and MMSE-NPI emerged as the most frequently employed instruments combinations. In PD trials, UPDRS was the most commonly used instrument, which was frequently used with PDQ, MoCA, CGI, and Time Up and Go Test (TUG). In ALS trials, researchers frequently utilized ALSFRS in conjunction with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Assessment Questionnaire (ALSAQ) and Handheld Dynamometry (HHD). In FTLD trials, the most commonly used instruments combinations were NPI and Clinical Dementia Rating Scale, as well as NPI and Clinical Global Impression (CGI). In LBD trials, the NPI-MMSE combination was frequently employed, while in HD trials, the UHDRS-CGI combination was the most commonly used.
Usage of different versions
Outcome measurement instruments typically contain multiple modules or various versions to address cultural differences, accommodate diverse populations, and enhance reliability and validity. For instruments such as CGI and PGI, which are instruments for assessing the overall severity of illness or improvement in clinical trials, and multiple versions for change (CGI-C, PGI-C), severity (CGI-S, PGI-S) and improvement (CGI-I, PGI-I) are available. When employing the MWT, the 10MWT was the most commonly used, although other versions such as the 4MWT, 6MWT, 30MWT, 4x3MWT, and 4x10MWT were also used. Similarly, for PHQ, the PHQ-9 was the most frequently utilized version, while the PHQ-2, PHQ-4, PHQ-8, PHQ-15 were also used